Abstract
Background: Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) has been classified as large B-cell lymphomas (LBCL) of immune-privileged sites according to the 5th edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification. The efficacy of high-dose methotrexate as a first-line treatment was suboptimal with a short effective remission time and low response rate. The recent discovery of the frequent copy number alterations in 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 and increased expression of PD-L1 in PCNSL provide the rationale to evaluate the efficacy of PD-1antibody in PCNSL.
Methods: NCT05347641 is an ongoing Phase II, single-center, single-arm, open-label study, aimed to enrolled an estimated 23 newly diagnosed PCNSL patients. Enrolled patients first received the Pen-RMA induction treatment, including rituximab 375 mg/m2, d0; methotrexate 3.5g/m2, d1; cytarabine 1‒2g/m2, q12h, d2-3; penpulimab (an anti-PD1 antibody of IgG1 isotype) 200 mg, d5; 21d/cycle, for six cycles. Patients aged 60 years or younger, with complete response (CR)/unconfirmed complete response (CRu)/partial response (PR) after six cycles of induction treatment then underwent autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) before maintenance treatment. The maintenance regimen was administered based on patient response to ASCT, or to induction therapy for patients aged 60 years or older. Patients who achieved CR after ASCT or induction therapy then received 8 cycles of penpulimab as maintenance therapy, and those with PR after ASCT or induction therapy received whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) combined with 8 cycles of penpulimab as maintenance. Treatment response was evaluated by brain MRI and FDG-PET and/or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination every three cycles of the induction treatment. The primary endpoint of this study was two-year progression-free survival rate. Baseline tissue samples and sequential CSF or plasma samples were collected for targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) at Nanjing Geneseeq Technology Inc.
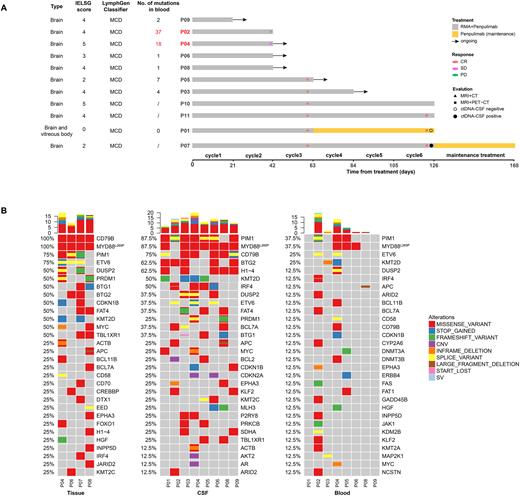
Results: Between April, 2022 and July, 2022, eleven newly diagnosed PCNSL patients has been enrolled. Treatment response was evaluable in eight patients. At the interim assessment point (after 3 cycles), six patients have achieved CR, with an overall response rate of 75.0%. Of these, three have completed 6 cycles of treatment and all achieved CR at the final assessment (Figure A). Adverse events of grade 3 or 4 occurred in five patients, including three neutropenia (27.3%), one thrombocytopenia (9.1%), and one renal dysfunction (9.1%). In the baseline samples, PIM1, MYD88L265P, and CD79B were the most common mutations, with a more comprehensive genomic landscape revealed by CSF than by blood (Figure B). All nine NGS-tested patients were classifier into the non-GCB subtype by the COO classification and the MCD subtype by the LymphGen classifier. CSF-based ctDNA monitoring was performed in two patients after 6 cycles of treatment. P01 had confirmed CR with ctDNA clearance in CSF. P07, was assessed as CR after 6 cycles, but the CSF ctDNA remained positive. This patient is currently receiving maintenance treatment and is being closely monitored for potential disease relapse. Interestingly, P02 and P04, who were PD and SD at interim evaluation, respectively, had markedly more mutations detected in their baseline plasma samples, indicating a poor prognosis (Figure A).
Conclusion: The induction treatment of Pen-RMA has shown excellent responses in newly diagnosed PCNSL patients with mild hematologic toxicity. Our preliminary results also suggested that CSF-based ctDNA could facilitate diagnosis when tissue was inaccessible and show higher sensitivity than imageology in assessing the depth of remission.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal